Analysis
To enable features, such as the integrated pseudocode disassembler and the class view, slicer creates in-memory models of classes.
By default, a partial version of the model is created for all classes in the background - this is called background analysis. When a class is to be disassembled or the like, a full version of the model is created and cached.
slicer also utilizes a copy of the JDK standard library (version 21) to improve output accuracy during disassembly. This can have a performance impact on initial disassembly, as the essential classes haven’t been fetched and cached - it can take longer.
Of course, you can also disable the usage of the standard library with the Analysis -> Fetch JDK classes option and rely purely on your workspace classes.
Search
Section titled “Search”Search allows you to search for identifying aspects of class files, such as constant pool values and class members.
The search tab can be opened like any unscoped tab, using Analysis -> Search or by pressing Ctrl+Shift+F.
There are three search modes, selectable in the dropdown menu:
- Partial match (case-sensitive)
- Exact match (case-sensitive)
- Regular expression (RegEx pattern occurrences)
and a special mode, only available for fields and methods, Reference. As the name implies, it searches for references of members instead of their declarations.
Strings
Section titled “Strings”Strings are the default, most basic search option. This mode searches for string entries in the constant pool, equivalent to string literals in the Java language.
This mode does not search in all string-like entries in the constant pool, so it will never find member names/descriptors or the like, only actual strings. If you wish to search for those, use the pseudocode mode.
Pseudocode
Section titled “Pseudocode”The pseudocode mode is useful for checking raw matches against the disassembled representation.
Currently, only the constant pool can be searched via this mode, as analysis results of the Code attribute are not available during search-time.
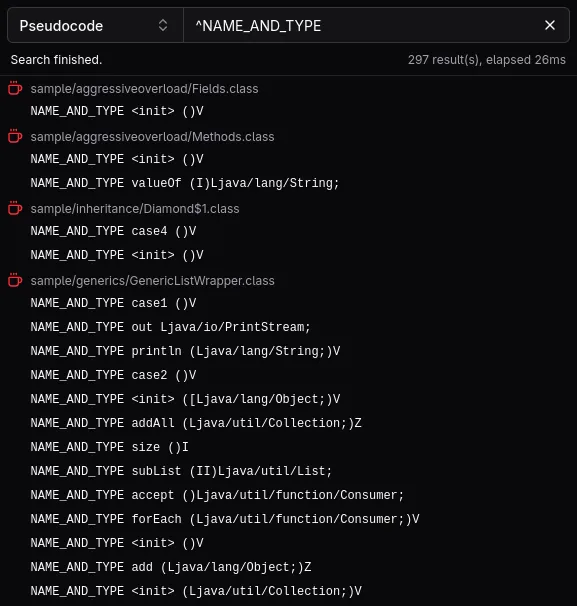
Commonly searched aspects and queries may look like this:
| Searching? | Mode | Query |
|---|---|---|
| All strings in the class file | Regular expression | ^STRING |
| All string-like entries in the class file | Regular expression | ^UTF8 |
| Reference to a specific class | Exact match/any | CLASS package/SearchedClass |
| Reference to a specific field | Exact match/any | NAME_AND_TYPE theField Lthe/Type; |
| Reference to a specific method | Exact match/any | NAME_AND_TYPE theMethod ()V |
Members
Section titled “Members”Members are searched by their name and descriptor, delimited by a space: theField Lthe/Type; or theMethod ()V.
Commonly searched aspects and queries may look like this:
| Searching? | Mode | Query |
|---|---|---|
| Any field/method with a specific name | Regular expression | ^theField |
| Any method returning a specific type | Regular expression | )Lthe/Type;$ |
| Specific field | Exact match/any | theField Lthe/Type; |
| Specific method | Exact match/any | theMethod ()V |
Transformers
Section titled “Transformers”Transformers are a convenient way to transform class files before they’re analyzed (just-in-time).
They can be applied in the Analysis -> Transformers menu.
slicer includes several options that may improve the chances of successful disassembly when dealing with obfuscated code.
Readability
Section titled “Readability”Readability transformers perform destructive transformations, which may help with readability of decompiled output in particular.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Strip annotations | Removes annotation-related attributes (*Annotations, AnnotationDefault), useful for mitigating “ASM crashers”. |
| Strip try-catches | Removes exception table entries in Code attributes, useful when dealing with flow obfuscation. |
| Strip local variables | Removes LocalVariable(Type)Table and MethodParameters attributes, useful when dealing with name obfuscation. |
| Strip synchronized blocks | Replaces all monitorenter and monitorexit instructions with pop instructions. |
| Strip generic signatures | Removes Signature attributes, useful when dealing with name obfuscation. |
| Strip debug information | Removes Deprecated, SourceFile, SourceDebugExtension and LineNumberTable attributes. |
Normalization
Section titled “Normalization”Normalization transformers perform functionally equivalent transformations, which mitigate common obfuscation techniques.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Verify attributes | Attempts to selectively strip attributes containing garbled data, mainly intended to mitigate “ASM crashers”. |
| Remove unnecessary modifiers | Removes ACC_SYNTHETIC and ACC_BRIDGE access modifiers where appropriate, useful when dealing with access obfuscation. |
| Remove unnecessary try-catches | Removes exception table entries with nonsense ranges and/or handlers that only rethrow the caught exception. |
| Remove unused local variables | Replaces local variable store instructions with pop instructions if the variables are never read. |
| No-op unreachable code | Replaces unreachable code with nop instructions. |
Verification
Section titled “Verification”The verification algorithm used in the Verify attributes transformer modifies the class file in an attempt to make it
readable by bytecode libraries that were not designed with JVMS violations in mind.
Violations of the class file specification are usually a product of an obfuscator attempting to thwart analysis, as in many cases, these class files are still readable by JVMs.
The transformer does the following:
- remove attributes that couldn’t be parsed
- remove attributes defined in an invalid context (e.g.
Codeattribute on an abstract method) - remove attributes with invalid constant pool references (index out of bounds, wrong entry type)